There are many forms of gene banks in the world. Some of them have a structure, and some are based on individual efforts to preserve old varieties on their own farms. Seed banks differ based on the method of storage and distribution of seeds, as well as on the protocols for preserving genetic resources.
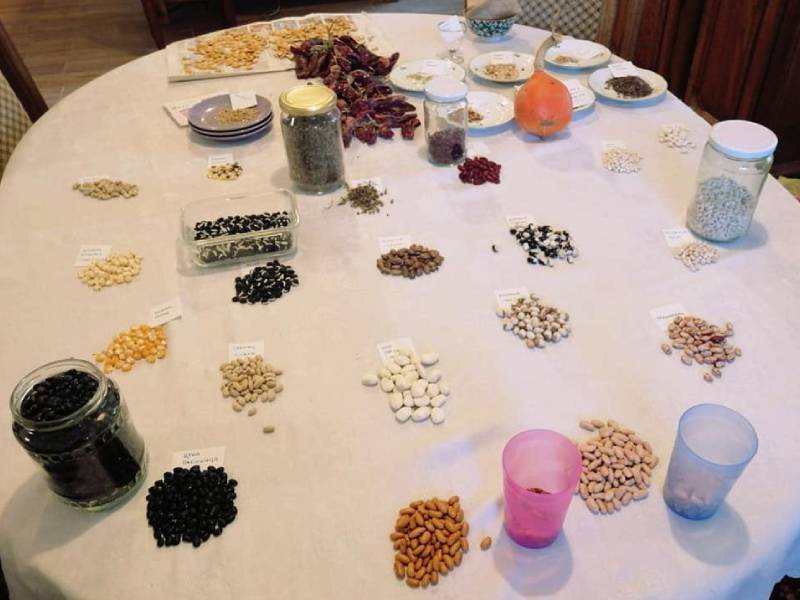

Based on the level of organization, gene banks can be divided into three types:
Individual gene banks.
Individual seed banks exist all over the world. They are based on the efforts of individuals to grow certain varieties on their farms for years, decades and centuries. Seeds are sometimes passed down through generations and this type of preservation of old varieties is the most dominant.
Institutional gene banks.
The second method is organized storage and preservation of seeds. It is mainly based on the institutional level. The holders of these seed banks are either state institutions such as institutes or the private sector that deals with seed production. They are usually equiped with facilities for long term storage of the seeds.
Community gene banks.
The third type is a form of organized preservation and exchange of seeds between farmers. This type of preservation of old varieties is not a discovery of the 21st century – farmers have always had some form of organization, although it was not recognized or organized in the form of a formal organization. Local gene banks are often shrouded in a veil of prejudice – sometimes experts are concerned community seed banks cannot ensure constant production and quality of seeds.
However, recent research shows that community gene banks are extremely resistant to change and that they enable a high level of success in preserving old varieties precisely because of the concept of plant material exchange.